Page 42 - Shelter, October 2024
P. 42
POLICY REVIEW
jobs and matching skillsets of 126 million (or, 29% of labour Even though literacy and
working population as well as force) was not even literate. education are important in
their improvement are critical. An additional 102 million order to become useful and
Therefore, the skillsets of (or about 24%) of labour productive human resource,
the young population in force had received either it is the functional skillsets
working age group need to be below primary or primary or functional capability that
developed, augmented, and level of education. In effect, is more important when it
nurtured through appropriate half of the labour force did comes to working in industry
education and skill training not have any level of skill and service sectors. Some
institutions as well as by acquired from the view point would acquire them on their
undertaking appropriate skill of educational compatibility own through by working
development programmes. required to perform any work voluntarily or with the
in organised/ unorganised help/ support from within
1.2 Education and skill sectors. The remaining labour or outside the family, some
development force had either middle acquire it through friends or
It is important to look at the level education (17.6%) or relatives, and some acquire
by referrals. Such acquired
structure of working age secondary level education skills on job are not formally
population or labour force (12%) or higher education recognised, therefore they
of the country in terms of (17%). Although the Right may get paid less or take very
general education that they to Education (RTE) Act of long time to get a recognition
have received, which plays the Government of India of their skills, all of which tend
an important role in their was expected to bring some to perpetuate exploitative
employability, productivity, change in the scenario to work conditions. Therefore,
and income generation some extent, it may take some there is a need for having
potential. It was estimated by more time to have any effect; vocational and skill training
Mehrotra et al (2013) that of but it only enables general institutions that impart
the 431 million working age skill formation up to middle/ skillsets to the population
population in 2009-10, nearly secondary level education. group within the working age.
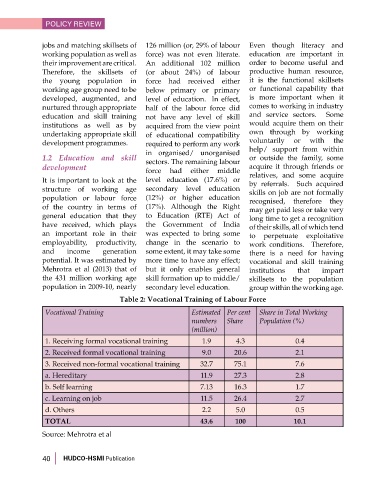
Table 2: Vocational Training of Labour Force
Vocational Training Estimated Per cent Share in Total Working
numbers Share Population (%)
(million)
1. Receiving formal vocational training 1.9 4.3 0.4
2. Received formal vocational training 9.0 20.6 2.1
3. Received non-formal vocational training 32.7 75.1 7.6
a. Hereditary 11.9 27.3 2.8
b. Self learning 7.13 16.3 1.7
c. Learning on job 11.5 26.4 2.7
d. Others 2.2 5.0 0.5
TOTAL 43.6 100 10.1
Source: Mehrotra et al
40 HUDCO-HSMI Publication