Page 74 - Shelter-April 2024
P. 74
CASE STUDIES
Increasing Global Extreme Weather Events: health and impacts human
Temperatures: The Climate change exacerbates services. Even if they haven’t
greenhouse effect is the extreme weather events, such contributed to greenhouse
process by which certain as heat waves, droughts, gas emissions it is the poorer
gases in the atmosphere floods, storms, and wildfires, people and developing
absorb and retain heat from making them more often and countries that are bearing a
the sun’s rays. Greenhouse catastrophic. Natural disasters disproportionate share of the
gas concentrations have are notorious for displacing burden of climate change [3].
risen due to deforestation, whole communities and
industrial gas emissions, wreaking havoc on vital 2. Urbanisation and
fossil fuel consumption infrastructure. Emissions
(coal, oil, and natural gas), The world is more
and other human activities. Loss of Biodiversity: Climate urbanised, which is causing
Sea level rise, ecological and change has altered marine, environmental degradation.
biodiversity impacts, more terrestrial and fresh water Overheating, glacier melting,
frequent and intense weather ecosystem around the world. steadily increasing global
extremes, and ice and glacier It has caused the loss of temperatures and other
melting are all results of a local spaces resulting in the problems are all consequences
steady increase in global climate driven extinction. of the carbon footprint of
warming [2]. This endangers the planet’s human activities.
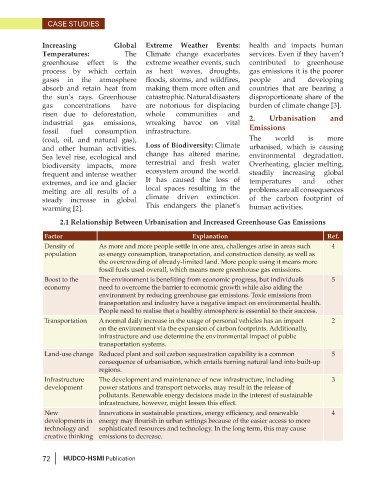
2.1 Relationship Between Urbanisation and Increased Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Factor Explanation Ref.
Density of As more and more people settle in one area, challenges arise in areas such 4
population as energy consumption, transportation, and construction density, as well as
the overcrowding of already-limited land. More people using it means more
fossil fuels used overall, which means more greenhouse gas emissions.
Boost to the The environment is benefiting from economic progress, but individuals 5
economy need to overcome the barrier to economic growth while also aiding the
environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Toxic emissions from
transportation and industry have a negative impact on environmental health.
People need to realise that a healthy atmosphere is essential to their success.
Transportation A normal daily increase in the usage of personal vehicles has an impact 2
on the environment via the expansion of carbon footprints. Additionally,
infrastructure and use determine the environmental impact of public
transportation systems.
Land-use change Reduced plant and soil carbon sequestration capability is a common 5
consequence of urbanisation, which entails turning natural land into built-up
regions.
Infrastructure The development and maintenance of new infrastructure, including 3
development power stations and transport networks, may result in the release of
pollutants. Renewable energy decisions made in the interest of sustainable
infrastructure, however, might lessen this effect.
New Innovations in sustainable practices, energy efficiency, and renewable 4
developments in energy may flourish in urban settings because of the easier access to more
technology and sophisticated resources and technology. In the long term, this may cause
creative thinking emissions to decrease.
72 HUDCO-HSMI Publication