Page 7 - Shelter-April 2024
P. 7
THEME PAPER
and hydrogen production are
expected to accommodate
variable renewable energy,
contributing to the need for
establishing a flexible and
resilient energy system.
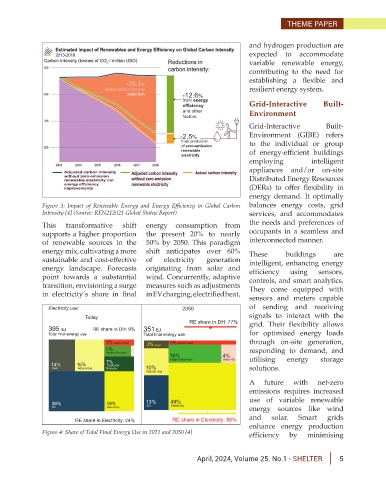
-12.6%
from energy
efficiency Grid-Interactive Built-
and other Environment
factors
Grid-Interactive Built-
-2.5% Environment (GIBE) refers
from production to the individual or group
of zero-emission
renewable of energy-efficient buildings
electricity
employing intelligent
appliances and/or on-site
Distributed Energy Resources
(DERs) to offer flexibility in
energy demand. It optimally
Figure 3: Impact of Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency in Global Carbon balances energy costs, grid
Intensity [4] (Source: REN212021 Global Status Report) services, and accommodates
This transformative shift energy consumption from the needs and preferences of
supports a higher proportion the present 20% to nearly occupants in a seamless and
of renewable sources in the 50% by 2050. This paradigm interconnected manner.
energy mix, cultivating a more shift anticipates over 60% These buildings are
sustainable and cost-effective of electricity generation intelligent, enhancing energy
energy landscape. Forecasts originating from solar and efficiency using sensors,
point towards a substantial wind. Concurrently, adaptive controls, and smart analytics.
transition, envisioning a surge measures such as adjustments They come equipped with
in electricity’s share in final in EV charging, electrified heat,
sensors and meters capable
of sending and receiving
signals to interact with the
grid. Their flexibility allows
for optimised energy loads
through on-site generation,
responding to demand, and
utilising energy storage
solutions.
A future with net-zero
emissions requires increased
use of variable renewable
energy sources like wind
and solar. Smart grids
enhance energy production
Figure 4: Share of Total Final Energy Use in 2021 and 2050 [4] efficiency by minimising
April, 2024, Volume 25. No.1 - SHELTER 5